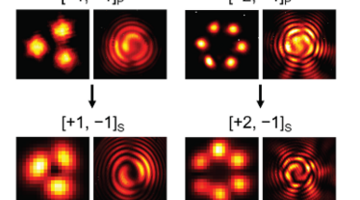
Brillouin vortex laser published in Laser & Photonics Reviews
Our new paper on a Brillouin vortex laser is published in LPR!
Abstract:
Optical vortices, which have been extensively studied over the last…
Coburger Physik-Studenten besuchen MPL
Die Gruppe kam im Januar an das MPL um mehr über die verschiedenen Forschungsfelder am Institut zu lernen.
Paper published in Physical Review Research
Our work on quantum dynamics of pulsed Brillouin scattering has been published in Physical Review Research today!
Quantum Optics meets Acoustics organized by Birgit Stiller, Wolfgang Löffler and Simon Gröblacher
Research group leader Birgit Stiller from MPL was one of the hosts of the Workshop „Quantum Optics meets Acoustics” at the Lorentz-Center in Leiden,…
Durchbruch bei der optischen Informationsübertragung: Einbahnstraße für optische Wirbel
Wissenschaftlern des Max-Planck-Instituts für die Physik des Lichts ist es erstmals gelungen, ein unidirektionales Bauelement zu schaffen, das die…
New paper on the arxiv: Exploring extreme thermodynamics in nanoliter volumes through stimulated Brillouin-Mandelstam scattering
Read about optoacoustics in different thermodynamic phases in toxic liquids and the interesting regime of negative pressure here!
Abstract:
Examinin…
Kontakt
Forschungsgruppe Stiller
MPI für die Physik des Lichts
Staudtstr. 2
D-91058 Erlangen