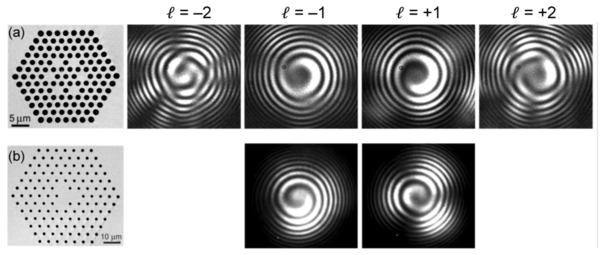
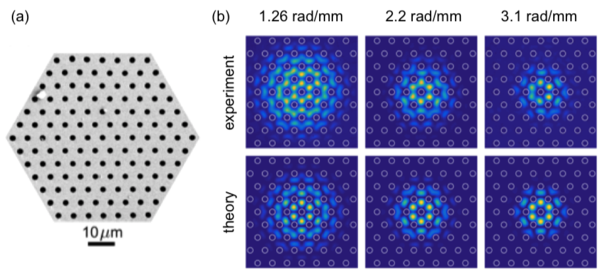
Multi-helical PCF and OAM
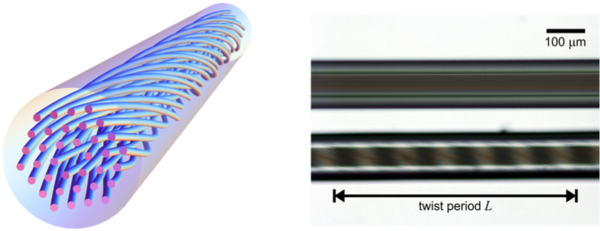
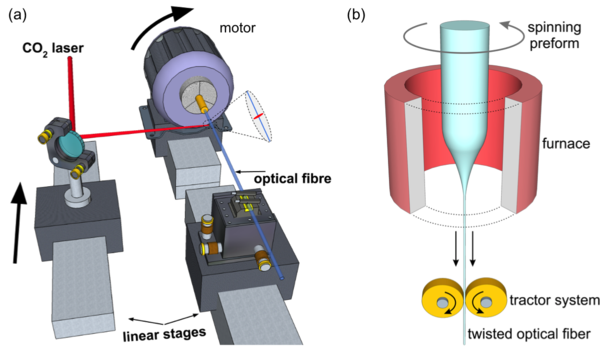
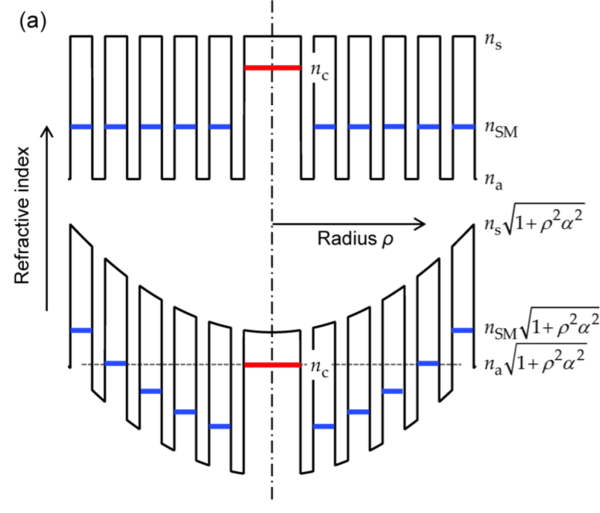
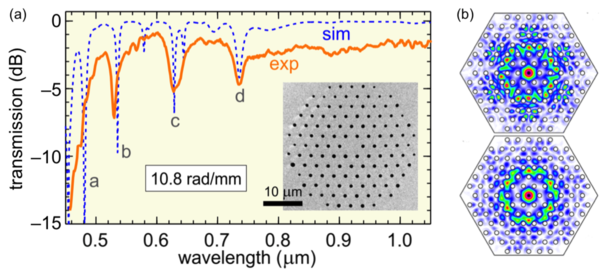
Chiral materials consist of many identical units (molecules or nanostructured elements) that are either randomly oriented in solution or arranged in an ordered fashion. They are ubiquitous in nature—for example, most biological molecules come in right and left-handed forms—and are finding an increasing number of applications in science and technology. Twisted photonic crystal fibre (t-PCF), in contrast, consists of a single uniaxial chiral unit that is infinitely extended in the third dimension—the direction of the twist. PCF itself typically consists of a hexagonal array of hollow microchannels running along the length of a glass fibre ~100 µm thick, so that when twisted it resembles a "multi-helix" of spiralling microchannels around a central axis. Over the past several years we have been studying the behaviour of light in a range of different types of t-PCF, in the process uncovering some surprising phenomena (for example, a PCF with no core that nevertheless guides light) and exploring potential applications. For a recent review see this paper.